What is an Environmental Impact Assessment | Objectives of EIA
What is Environmental Impact Assessment?
An environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) is an evaluation of policies, procedures, programs, or projects that affect the environment before deciding to proceed with a proposed action.
In this context, the term “environmental impact assessment” (EIA) is often used when applied to real projects carried out by individuals or companies, and the term “strategic impact assessment” (SIA) is often used for those processes, programs, and programs. Proposed by government agencies.

It is used in environmental management as part of project approval and decision-making. Environmental investigations may be subject to administrative rules regarding public participation and decision documents and may be subject to judicial review.
Evolution & History of Environmental Impact Assessment
Environmental impact assessment is considered one of the greatest political developments of the 20th century. The main goal of environmental impact assessment is to protect the environment and achieve the best combination of economic and environmental costs and benefits. Read the following to understand the evolution and history of the Environmental Impact Statement.
- EIA started in the 1970s. In 1969, the United States passed the first law, the National Environmental Policy Act of 1969 (NEPA).
- EIA was first implemented in developed countries but slowly started to be done in developing countries including India.
- Colombia and the Philippines are the first examples of developing countries to include EIA in their policies. It was introduced in 1974 in Colombia and 1978 in the Philippines.
- Worldwide, EIA is now used in more than 100 countries. In the mid-1990s, about 110 countries used EIA as their main environmental policy.
- In 1989, the World Bank approved EIA as a major development project.
Importance of Environmental Impact Assessment
Followings are the importance of EIA
- Environmental Impact Assessment connects the development environment with a healthy environment and sustainable development.
- EIA provides a cost-effective way to eliminate or minimize the negative impacts of development projects and facilities.
- It is government policy to obtain EIA approval from the Ministry of Environment before an industrial project is approved by the Planning Commission.
- Environmental Impact Assessment can be an important part of environmental management and its forecasting.
- EIA allows decision-makers to assess the environmental impact of development activities before embarking on a development project.
- Environmental Impact Assessment encourages the use of mitigation strategies for development planning.
- Environmental Impact Assessment ensures that development plans are environmentally friendly and within the limits of ecosystem harmony and regenerative capacity.
- EIA is a tool used to assess the environmental impact of development plans and projects.
- It creates efforts to prevent or minimize damage to the environment and organisms and to promote human health and well-being.
- EIA aims to enhance the importance of the country’s ecosystem and natural resources and to create an appropriate institutional framework to achieve this goal.
Objectives of Environmental Impact Assessment
- Identify, forecast, and assess the impact of economic, environmental, and social development activities.
- Provides information on environmental impacts for decision making
- Promote sustainable and sustainable development by identifying appropriate mitigation options and actions. Identify, forecast, and assess the impact of economic, environmental, and social development activities.
Project Level of Environmental Impact Assessment
In many countries around the world where EIA is used, development projects such as road and highway construction, ports, energy projects, factories, mining projects, etc. are assessed from the environment before being implemented and implemented. . . . The EIA then recommends appropriate measures to minimize or control and control the curriculum. Examples of these changes are:
- Traffic changes
- Drawing up emergency procedures in case of oil leakage in the port
- Reducing the height of the dam
- Ensure that the affected people are rehabilitated
- This applies to fuel substitution in electric generators
Environmental Impact Assessment Processes
The EIA includes various steps outlined below. However, the environmental impact assessment process is cyclical with interactions between different stages.
- Screening
- Scoping
- Collection of Baseline Data
- Impact Prediction
- Mitigation measures and EIA report
- Public hearing
- Decision Making
- Follow-up and implementation of the Environmental Management Plan
- Alternative Valuation and Environmental Impact Assessment
- Risk Assessment
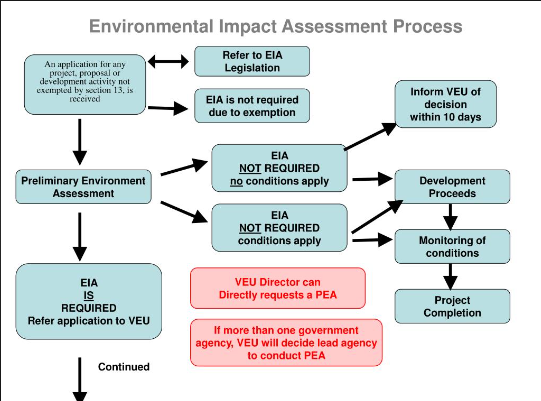
Screening
Project plans are carefully reviewed about investment size, location, and type of development and if the project requires regulatory approval, an investigation is required. Consists of determining the projects or development plans that require a full or partial impact study.
Scoping
This step in the EIA process is necessary to determine whether to balance the negative impacts on biodiversity (including the option not to promote development) by finding alternative projects or sites that do not avoid the negative impacts or balance the adverse effects) and, finally, suppress how it is referenced to impact assessment. The scope is knowledge of the potential impact of the project, the area of impact, mitigation, and any monitoring requirements.
Collection of Baseline Data
Environmental Impact Assessment includes the collection of the baseline data.
Impact Prediction
It is important to predict and explain the expected negative and positive, reversible and irreversible, and temporary and permanent effects of a well-understood project plan. Anticipate and identify the environmental impacts of the proposed project or development plan, including a detailed description of alternatives.
Mitigation Measures and EIA Report
The final EIA report must contain measures and procedures to prevent, reduce or prevent impacts or other environmental damage or compensation. This report also includes an environmental policy and a summary of non-technical information for the public.
Public Hearing
At the end of the EIA report, the community and environmental groups living near the project site should be informed and consulted. During the public hearings, the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) should be evaluated with the definition of the project (scope) and the participation of the public (including the authorities).
Decision Making
In the decision-making process, the Impact Assessment Committee consults the responsible project manager with experts and advisors and makes a final decision based on the factors of Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) and Environmental Management Plan (MBP). In doing so, it decided whether the project was approved and, if so, under what conditions.
Monitoring and Implementation of an Environmental Management Plan
Monitoring different phases of implementation and application, e.g. B. Design, research, construction, etc It is monitored whether the expected effects and the proposed mitigating measures are met as described in the Environmental Management Plan (MBP). Compliance with the EMP will be assessed to ensure that unintended effects or failed mitigation actions are identified and addressed promptly.
Alternatives Assessment and Environmental Impact Assessment Report
Potential alternatives must be identified and environmental characteristics compared for each project and development program. Alternatives should include both project location and processing technology. If other solutions have been explored, a mitigation plan for the selected alternative should be developed, complemented by an Environmental Management Plan (EMP) that guides the proponent toward environmental improvements.
Risk Assessment
The inventory analysis and index also form part of EIA procedures.

FAQs
Q: What is an EIA?
Ans: An environmental impact assessment or EIA is a process used to assess the environmental impact of a proposed activity. It takes into account the socio-economic, cultural, and human health impacts.
Q: When was EIA introduced in India?
Ans: EIA was introduced in India in 1976-77 when the Planning Commission instructed the Department of Science and Technology to assess river basin projects from an environmental point of view. It was later extended to all projects requiring approval from the Public Investment Council.
Q: Who is responsible for EIA in India?
Ans: The Union Ministry of Environment and Forests (MEF), Government of India, has issued an EIA Notice under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986, for the expansion or renovation of an activity or the establishment of new projects for the System Environmental Clearance (EC) Required. The verdict is January 27.
Q: What is the main purpose?
Ans: The main goal of EIA is to protect the environment and achieve the best combination of economic and environmental costs and benefits.
Q: Is EIA only for developed countries?
Ans: EIA was initially accepted by developed countries but has gradually been accepted by developing countries, including India.