Heart Attack, Symptoms, Causes, Risks and Treatment
Heart Attack
What is Heart Attack?
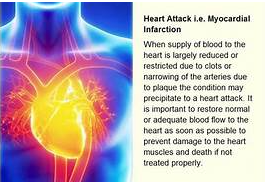
A heart attack occurs when one or more arteries in your heart become blocked. As a result, your heart doesn’t get enough oxygen. It’s important to understand that your heart attack may not be a one-time occurrence. Even if you survive a heart attack, you still have an increased risk of having another attack. With the right medication and lifestyle changes, you can help reduce your risk of having or dying from an attack.
Also, Read
- Biological Molecules and its Types, Concepts of Biology
- Nephrology and Nephrology Education and its related Diseases
Causes of Heart Attack
Coronary heart disease is the cause of most heart attacks. In coronary artery disease, one or more arteries in the heart are blocked (coronary artery). This is usually caused by cholesterol-containing deposits called plaque. The plaque can narrow the arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart.
If the plaque ruptures, it can cause a blood clot in the heart.
A heart attack can be caused by a complete or partial blockage of an artery in the heart (coronary artery). One way to classify a heart attack is if the electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) shows a specific change (ST disparity) that requires urgent invasive treatment.
An Acute complete blockage of a medium or large coronary artery usually indicates that you have an ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI).
A partial blockage usually indicates that you have a non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI). However, some people with NSTEMI are completely turned off.
Complications
Complications of heart disease are often caused by damage to the heart muscle. Possible complications of heart disease include:
Irregular or atypical heart rhythms (arrhythmias): Heart rhythm disorders affect the way electrical signals pass to the heart, causing changes in the heartbeat. Some can be serious and even fatal.
Heart Attack: This strange condition occurs when the heart cannot suddenly and easily pump blood.
Heart Failure: Severe damage to the heart muscle can cause the heart to be unable to pump blood. Heart failure can be temporary or permanent.
Inflammation of the material similar to the sac around the heart (pericarditis):
Sometimes heart disease affects the weak immune system. This condition can be called Dressler’s syndrome, heart attack syndrome, or post-injury syndrome.
Cardiac Arrest: Without warning, the heart stops. Sudden cardiac arrest is caused by a sudden change in heart symptoms. Heartburn increases the risk of having this life-threatening condition. It can cause death (sudden death of the heart) without medical attention.
Risk Factors for Heart Attack
Certain medical conditions, lifestyle, age, and family history can increase your risk of heart disease and stroke. These are called risk factors. Half of Americans have one of three risk factors for heart disease: high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and smoking.
Some risk factors, such as age or family history, cannot be controlled. But you can take steps to reduce your risk by changing factors you can control.

Learn more about heart disease and attack risk factors.
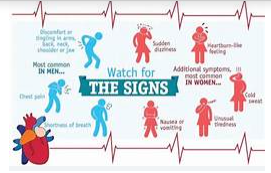
Symptoms in Women
Women may experience many, many, few, or none of the common symptoms of heart disease. Some type of chest pain, pressure, or discomfort is still a common symptom of heart disease in women. However, many women have symptoms of heart disease without chest pain. Symptoms of heart disease in women can include:
- Pain in the neck, back, shoulders or jaw
- Shortness of breath
- Stomach pain or heartburn
- Pain in one or both arms
- Nausea or vomiting
- Nausea or dizziness
- Unusual or unexplained fatigue that can last for several days
Older adults and people with diabetes may have no or very mild heart symptoms. Do not ignore the symptoms of a heart attack, even if they are not serious.
Angina vs. Heart attack
Chest pain caused by a decrease in blood flow to the heart muscle is called angina. This is a common symptom of heart disease.
Persistent angina, the most common and most common type of angina, often occurs during exercise or stress.
Unexpected unstable angina should be treated as emergency medical care
An angina attack can feel like a heart attack, and it can often be difficult to distinguish between angina and an actual attack, especially with unstable angina.
If you have persistent angina that occurs during exercise and is relieved by rest, you may think that sudden chest pain is just a short attack of angina. If your chest pain persists after resting or lasts for more than 10 minutes, you may have an attack.
Talking to your doctor about how to treat angina can help you better understand the symptoms of angina and heart attack and prepare if chest pain is a sign of an attack of the heart
Conclusion
Hope so, you have read the topic carefully. I have tried my best to provide you with authentic information regarding to the heart. If you have any questions related to this topic you can ask.