Difference between ingrown hair and genital warts
The difference between ingrown hair and genital warts is that both are similar in appearance, are vastly different in all other respects. Ingrown hairs are hairs that curl inward or grow sideways into the skin.
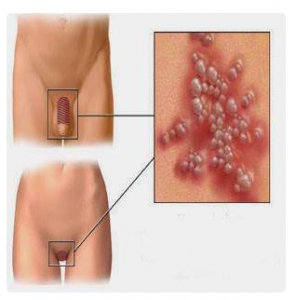
Genital warts, also known as condyloma acuminate or genital warts, are symptoms of a highly contagious sexually transmitted disease caused by certain types of the human papillomavirus (HPV).
Also Read: Difference between worker and employee
Also Read: Difference between RN and BSN
1: Difference in Causes
The major difference between ingrown hair and genital warts is that in Ingrown hairs result from shaving, waxing, very tight clothing, or any such procedure that causes uneven breaking of the hair with sharp points. Subsequent shaving forces these hairs below the surface of the skin. Ingrown hairs are more common in people with curly or coarse hair.
Genital warts, on the other hand, are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), which is transmitted through skin-to-skin contact during oral, genital, or anal sex. In children under the age of 3, HPV can be transmitted through direct manual contact, but sexual abuse should also be suspected. The risk factors for developing genital warts are multiple sexual partners, sex at an early age, and a weakened immune system due to certain diseases or drugs.
2: Difference in Manifestations
Ingrown hairs create a reddish patch on the skin that looks like a pimple. In men, they affect the cheeks, chin, and neck. In women, ingrown hairs develop on the lower limbs, pubic area, and armpits. The most common symptoms are itching, hair that remains despite shaving. Ingrown hairs are never a serious condition, but they can become irritating and embarrassing when they leave dark skin or scars.
Genital warts affect both men and women. After exposure to the HPV virus through sexual contact with an infected partner, there is a latency period of a few weeks to a few months during which warts will not be visible externally. Genital warts are painless, itchy, and rarely bleed. The affected areas are the penis, urethra, scrotum, vulva (the external part of female genitalia), labia (external folds of the vulva), vagina, cervix, and area around the anus. These warts r ange in size from 1mm to several centimeters when many join together. Genital warts can be soft or hard, and some appear cauliflower-like.
Also Read: difference between tequila and mescal
Also Read: Difference between freckles and moles
3: Difference in Treatment
Ingrown hairs will resolve on their own if left untreated. They can be removed with tweezers or by making a small incision at the hair site with a needle or scalpel to release the hair. If an ingrown hair becomes infected, anti-inflammatory medications and antibiotics may be needed. Close shave or use too much force while shaving.
Genital warts are diagnosed based on their location and appearance, but investigations such as enlargement of the area, biopsy, pap smear in women, etc. can be done to aid in diagnosis. Aside from certain medications, techniques like freezing, laser resurfacing, and surgical removal are used to treat genital warts. However, there is no cure for genital warts, and the above treatment methods only cause temporary disappearance. Genital warts reappear after a few months or years.
4: Other Difference between ingrown hair and genital warts
Even the slightest change in the genitals is enough to cause most of us to panic. After all, it could be anything – ingrown hair, a pimple, or maybe even genital warts. Of course, the latter is especially scary, but trust me, it’s definitely not the end of the world.
Genital warts or genital warts are the result of an infection with human papillomavirus (HPV), explains Dr. Ana G. Cepin, Assistant Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology at Columbia University. “HPV is made up of multiple strands that can form different things in the body,” she continues. And some of these strands are responsible for uncomfortable genital warts.
The good news: an HPV vaccination not only protects you against cervical cancer but also against genital warts! So, to make sure you don’t get infected, you should get vaccinated. However, if you are struggling with a genital wart or think you may have one, you should seek medical advice as soon as possible. This is where all the necessary measures are taken to get the virus under control and prevent future outbreaks.
Since dealing with the topic can be stressful enough for you, Dr. Cepin step by step what to do in case of a genital wart.
Summary
Ingrown hairs result from a mechanical cause, such as shaving and waxing, which can cause hair to grow under the skin and create a sore. They resolve the problem themselves unless they become infected, which requires the use of antibiotics. Genital warts are caused by the human papillomavirus, which is transmitted through sexual contact. These warts can go unnoticed for several years as they are painless and rarely bleed. Genital warts cannot be cured. They disappear after taking medication or surgery and reappear after a few months.
Also Read: Difference between homicide and murder
Also Read: Difference Between Java and JavaScript