What is Acid Rain? Definations, Causes and Effects of Acid Rain
Acid rain is rain or other types of rain that do not contain sugar, i.e. high in hydrogen ions (low pH). Most water, including drinking water, does not have the same pH between 6.5 and 8.5, while bitter rain has a low pH of 4-5 on average. The higher the acidity of the toxic rain, the lower the pH. Toxic rain can damage plants, aquatic plants, and crops. Acid rain produces sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, which react with water molecules in the air to form acids.
What is Acid Rain?
Acid rain or acid deposition is a general term encompassing all forms of precipitation where acidic components such as sulfuric acid or nitric acid fall from the atmosphere in wet or dry form. This can be rain, snow, fog, melting snow, or acidic soil.
Also read:
- Environmental Monitoring, Reasons and Protections, Environmental Sciences
- Why is Ozone Layer Important? Environmental Sciences?
- Environmental Health and Safety (EHS) And its Implementations
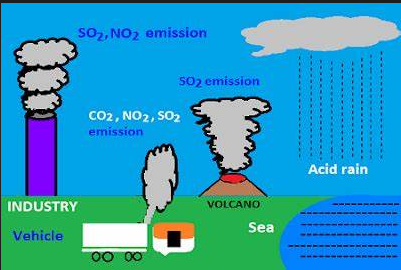
What are Causes of Acid Rain?
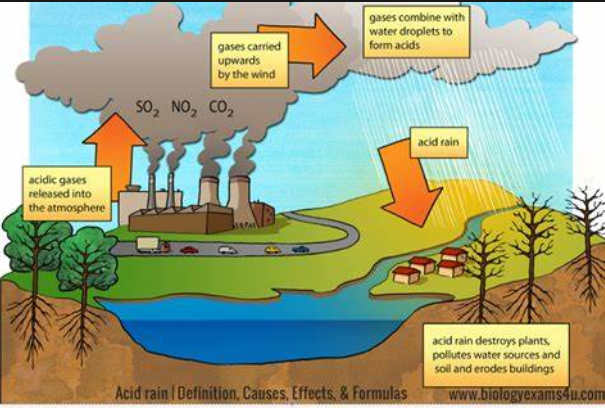
Acid rain occurs when sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogenous nitrogen (NOX) are released into the air and carried through the air. SO2 and NOX absorb water to produce sulfuric acid and nitric acid. The answer is oxygen and other drugs. Then mix it with water and other ingredients and leave.
Small amounts of SO2 and NOX cause rains from natural areas such as volcanoes, but most come from fires. The main sources of SO2 and NOX in the air are:
- In fields that burn to generate electricity, Two-thirds of the SO2 and one-quarter of the NOX in the air come from electricity.
- Heavy vehicles and equipment
- Industry, oil, and other industries
- Winds can push SO2 and NOX away from other boundaries, making acid rain a problem for everyone, not just those close to the market
Effects of Acid Rain
- Acid rain affects agriculture and is extremely harmful to plants and organisms. It deprives plants of all the nutrients they need to grow and survive. Acid rain affects agriculture and alters soil structure.
- This causes respiratory problems in animals and humans.
- When rain reaches rivers and lakes, it affects the aquatic environment. It basically damages the body of aquatic organisms and changes the structure of water chemicals in a way that contaminates the water body.
- Acidic water damages water and iron pipes, but also heavy metals such as explosives and copper from drinking water.
- Damage to stone or metal buildings and monuments
Measuring Acid Rain
Acidity and alkalinity were measured using a neutral pH scale of 7.0. The lower the pH of a substance (below 7), the more acidic the higher the pH of a substance (7 or higher), It is more alkaline. The pH of normal precipitation is about 5.6. It is slightly acidic because it is soluble in carbon dioxide (CO2). Acidic water usually has a pH between 4.2 and 4.4.
Policymakers; researchers, Ecologists, and modelers rely on the National Atmospheric Infiltration Program (NADP) National Trends Network (NTN) to measure water output. NADP/NTN is in the United States; Canada Alaska Brine is collected at more than 250 study sites in Hawaii and the US Virgin Islands.
Unlike water conditions, drainage is difficult to measure and expensive. Dry area estimates for nitrogen and sulfur pollution are provided by the Clean Air and Trends Network (CASTNET). Atmospheric conditions are measured by Castanet at over 90 locations.
Accumulated acids are washed away in lakes and rivers, which can release other acids. The Long-Term Monitoring (LTM) network measures surface water chemistry at more than 280 sites and provides critical information on the health of aquatic ecosystems and how they respond to changes in water acidity.
WHAT USGS AND OTHERS DOING ABOUT ACID RAIN?
Scientists in many disciplines study acid rain and its effects. The National Acid Rain Assessment Program (NAPAP) is a federal program with representatives from more than 12 federal agencies that fund studies on acid rain formation and its impact on lakes, crops, forests, and equipment. Acid rain can affect historic buildings because buildings and monuments cannot adapt to changes in the environment, such as plants and animals. Scientists are researching effective control techniques to limit emissions from power plants and vehicles that cause acid rain.
We will also consider the implications and benefits of regulations requiring the prevention of air pollution. Finally, scientists study the destruction process to find effective ways to protect and restore historic buildings and monuments. The National Park Service and other agencies responsible for the protection and preservation of national monuments are not particularly concerned about the effects of acid rain but are interested in historic buildings and the best options for preserving them.
Solutions to Avoid Acid Rain
The only way to combat acid rain is to limit emissions of the pollutants that cause the rain. This way indicates only a few fossils are to burn.
In the United States, the Clean Air Act of 1990 targeted rain and imposed pollution limits that reduced sulfur dioxide emissions by 88% between 1990 and 2017. For example, this trend has helped New England spruce forests and fish recover from damage from acid rain. But recovery takes time, and the northeastern United States and eastern Canada have only recently shown signs of nutrient stabilization.
Acid rain will remain a problem as long as fossil fuels are used, and countries like China, which rely heavily on coal and electricity to produce electricity and steel, are still grappling with its effects. Deadly landslides in China in 2009 may have been caused by acid rain, a study finds. China has seen its sulfur dioxide emissions fall by 75 percent since 2007, while India’s has halved.