Disaster Management, Prevention and Mitigation
What is Disaster Management?
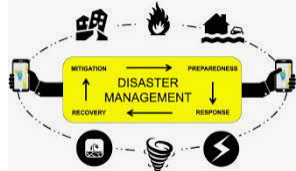
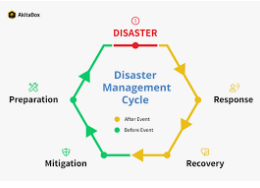
Disaster management is to reduce or prevent the chance of damage caused by an accident, to help victims quickly and adequately and to recover quickly and efficiently. The disaster management cycle represents an ongoing process through which governments, businesses and civil society organizations can prepare for and mitigate the effects of disasters, respond quickly to weather events and disasters, and take action to mitigate disasters.
According to the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies, natural disasters are natural phenomena that occur spontaneously as a result of fast or slow events that affect human health and lead to adverse consequences. Death and other suffering. These risks include:
- Geophysics (e.g. earthquakes, earthquakes, tsunamis and volcanoes)
- Hydrology (including floods and floods)
- Climate (e.g. extreme heat, drought and forest fires)
- Meteorology (e.g. hurricanes and storms/waves)
- Biological (e.g. Disease Epidemics and Insect/Animal Plagues)
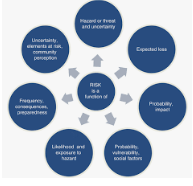
United Nations Office on the Reduction of Hazardous Substances Natural disasters are determined by size or severity, frequency, duration and severity, ie. Landslides are short-lived and usually occur in small areas, but in the event of a drought they disappear and affect large areas:
Man – Made Accidents
According to the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies, man-made accidents are human activities that take place in or near human settlements and are often caused by the environment or humans. It should look like this:
- Environmental pollution
- Pollution
- Hazardous materials (eg hazards to industry, machinery and transport associated with the manufacture, use or transport of hazardous materials).
Also Like,
- Habitat, Component and Types of Habitat
- Environmental Development and Sustainability
- Eco-Friendly Energy
Prevention Strategies from the Disasters
We optimize and prevent damage and pain caused by these infections. Emergency management cannot prevent an accident, but it can prevent it by ignoring important issues and managing the process. Information on actions to reduce the impact of the collision. The use of measuring instruments reduces the severity of collisions.
Here are some examples of disaster victims to protect vulnerable communities and reduce free time:
- Learn about threats and how to deal with them
- Inform the public to be prepared for any emergency
- Action and response to warnings and objections
- Terrorism and risk management are designed to reduce the risk of at-risk communities. These include:
- Encourage community members to purchase the insurance they need to protect their property and products
- Teach families and businesses to be better prepared for disasters
- Encourage the use of protective equipment in construction
- It supports maintenance activities such as construction and storage
- Establish interregional contacts and work with politicians in relevant countries, governments and regions.
Critical Infrastructure
Intensive structural protection in the event of a disaster can mean the difference between life and death. Particular attention should be paid to disaster response, including critical programs and resources related to the economy, security and public health of local communities.
For example, installing safety measures to minimize damage to water and sewer systems or nuclear power plants can prevent serious consequences.
For example, after the 2011 earthquake and tsunami, Japan suffered severe physical and mental damage. The flood cut off electricity from Daiichi’s cooling systems in Fukushima, causing a major nuclear disaster.
Objectives of Disaster Management
The project aims to develop four types of policies and guidelines, namely “National Disaster Management Plan” as a national policy and official guideline for holistic disaster response and governance in Pakistan, “Early Warning In Case of Multiple Disasters “and Human Resource Development Policy in Pakistan. Policies “such as guidance and policies to improve human resources and” Community-based Strategic Disaster Risk Management “to create community-based disaster risk management